A triangle limit
Collection
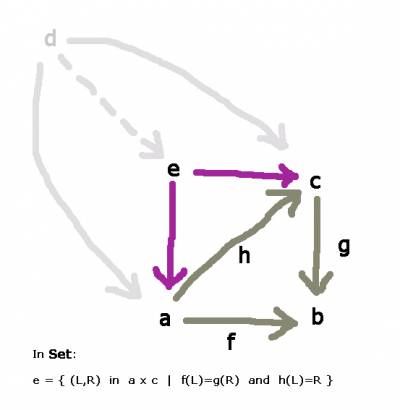
Consider the circle graph with 3 vertices $a,b,c$ and 3 edges.
There are, up to relabeling, two directed versions of it:
- The graph where all arrows go in one direction, say
$h:a\to c$
$g:c\to b$
$f:b\to a$
- The graph where one of the arrows point in another direction, say
$h:a\to c$
$g:c\to b$
$f:a\to b$
so that both $f$ and $g$ point at $b$.
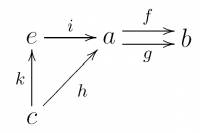 If $h$ is an isomorphism $h:c\simeq a$, then we can replace $c$ by $a$ and we're left with a pullback. This can also be viewed as a two-parallel-arrows situation, and it is called the equalizer.
If $h$ is an isomorphism $h:c\simeq a$, then we can replace $c$ by $a$ and we're left with a pullback. This can also be viewed as a two-parallel-arrows situation, and it is called the equalizer.
In ${\bf{Set}}$, if $h$ is an iso, the object is $e=\{x\in a\ |\ f(x)=g(x)\}$. For general $h$, the object is a subset of the pullback $a\times_b c$, and thus in particular a subset of the Cartesian product $a\times c$.
$e=\{\langle x,y\rangle\in a\times_b c\,\mid\,h(y)=x\}$
or
$e=\{\langle x,y\rangle\in a\times c\,\mid\,f(x)=g(y)\land h(y)=x\}$