Presheaf . topology
Collection
| context | $\langle X,\mathcal T\rangle$ … topological space |
| context | ${\bf C}$ … category |
| definiendum | ${\bf C}^{\mathrm{Op}(X)^{\mathrm{op}}}$ |
Discussion
Motivation via fibre bundles
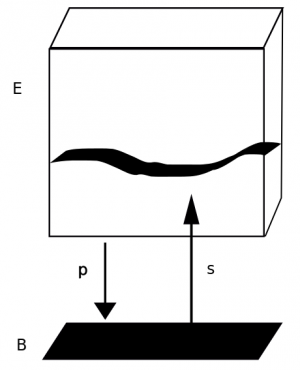
Let $\langle X,\mathcal T\rangle$ be a topological space. A fibre bundle
$Fib\to E\to X$
is given by a projection map $p:E\to X$ together with, for each open set $U\in \mathcal T$, the possibility to locally identify $E$ as $U\times Fib$ (pic related). With this fibre point of view, we want to speak of particular functions $X\to E$, namely the sections $\sigma$ which satisfy $p\circ\sigma=\mathrm{id}_X$.
In the simplest case, when globally $E=X\times Fib$, we can define a section $\sigma:X\to E$ of the bundle via $\sigma(x):=\langle x,s(x)\rangle$ and here we can simply take $p:=\pi_1$. Clearly, $\sigma$ is determined by a function $s:X\to Fib$ into the fibre.
If the the bundle has non-trivial topology and the fibres over $X$ are twisted, then there can't be a global function $s:X\to Fib$ determining the section $\sigma$. However, each section is still fully determined by a collection of local such functions $s|_U:U\to Fib$. Note that the function space $U\to Fib$ is the object image of $U$ under the contravariant hom-functor $\mathrm{Hom}_{\bf{Set}}(-,Fib)$ to ${\bf{Set}}$.
A sheaf $F$ is a particular kind of contravariant functor which helps to capture sections. The object image $FU$ of a sheaf of a an open set $U$ is a local function space.
Examples
- Consider the sheaf $C^\infty$ of all smooth functions over $X$. If $U$ is an open set of $X$, then the objects $C^\infty U:=\{f:U\to\mathbb R\ |\ f\dots\text{smooth} \}$ is the restriction of such functions to $U$.
- Any continuous function. Take $X=\mathbb{C}\setminus\{0\}$, $E=\mathbb C$, and $p=\exp$. Define a the sheaf $\Gamma(E/X)$ via $\Gamma(E/X)U:=\{s:U\to E\ |\ p\circ s=\mathrm{id}_U\}$. Then $\Gamma(E/X)U$ is the set of branches of the logarithm on $U$.
Sheaf theory is used for discussing the idea of analytical continuation and applying it too subjects which don't necessarily have to do with complex numbers. The image of the functor can contain other objects than sections (e.g. the spaces may be vector bundles as in K-theory, or spaces of differential forms, etc.) and the category itself doesn't have to be a classical topological space (see Grothendieck topology).
Notation
For the purpose of defining seperated presheaves of sections, we use the following notation:
If $i\in \mathrm{Op}(X)^{\mathrm{op}}[V,U]$ is an inclusion $i:V\to U$ of a smaller open set $V\subseteq U$ in $U$, then it's fmap image $F(i):{\bf C}[FU,FV]$ should be understood as restriction of function domain. So if $s\in FU$, we write $s|_V$ for $F(i)(s)$.
Reference
Wikipedia: Sheaf